



 (4 ratings)
(4 ratings)
The mechanical equipments designed by the humans are some of the most happening objects for the technology. The automotive engine is one of the most beautiful creations, which shows the perfection of generating such a great amount of power from dwarf architecture. It’s wonderful to imagine the power of a huddle of horses transmitted in a diminutive geometry. Well, the never ending technology has proven itself many times and in many ways. Though, the engines are of many types and most of them are built for a specific purpose. There’s a hell lot of confusion in all these versions, but the main objective to which we are going to tuck here will be the flat engines. A short journey of flat engine’s introduction is worth mentioning, which can be followed up here.
The V-series engines are usually assembled in the shape of the English language alphabet “V”. This means that the crankshaft keeps itself located at the bottom point where both the leaning lines meet, and these leaning lines serve the purpose of pistons. Now, the angle between the pistons is immaterial as it varies from manufacturer to manufacturer and their particular needs. The pistons run inside a cylinder so the angle can also be measured with that. Some bikes use acute angles, some use obtuse while some use right angled ones. It completely relies over the manufacturer’s exclusive predilection. The arrangement of cylinders in this format saves the space and reduces the size and height of the engine, so that it can perform better while using the concept of the inline configuration in compact terms.

The engine can be brought to a flat position where the angle between the engines comes out to be 180 degrees. At this position, the pistons seem to be running opposite to one another’s face. Most of the people know that the functioning of an engine comprises of 4 stages; Intake, Compression, Ignition and Exhaust. This happens in all the cylinders. The V engine is no different to that. When it comes to flat engine, the things could vary a bit when compared to one of its own branch with respect to the timings of these stages in consecutive cylinders. Here, I am talking about the BOXER ENGINE.

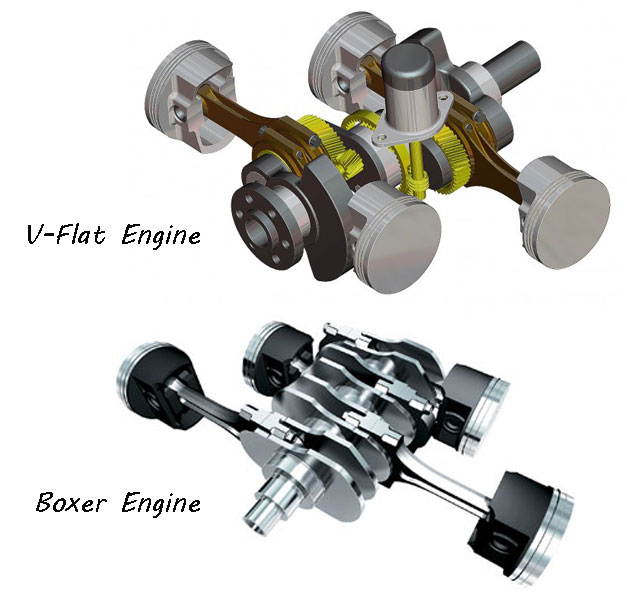
The flat engine and the Boxer engine have some good points to distinguish. The weight management aspect was also under the consideration during the creation of this engine as the functioning of these two is varied that way. You must be thinking of, if a boxer and a flat engine share the same procedure, i.e. being based over the V series 180 degree platform, then what’s the big deal? How are they different? Actually, the Boxer engine is built with two crank pins for two cylinders while the flat engine works over single crank pin for two cylinders. Try to make out the differences with the following images.

The first image is a boxer engine. The first sets of pistons connect to the single crank pin. Same goes with the next two. This means that direction of movement of both these engines will be in the opposite directions as they are linked at parallel positions. The second image is a V12 flat engine. Each set of two pistons is connected at the same spot or crank pin. The movement of these pistons will look like a to and fro motion where they will move in accordance with the direction of one another. In the boxer engine, the piston moves opposite to each other reflects that the weight will remain constraint at either center or on the both sides.

The V series engine is a 2 century old concept, which gave birth to Boxer series during the late 18th centenary. These engines were crafted to deliver maximum power while occupying minimum space, weight and cost compared to inline engines. The zigzag arrangement endows good space between the cylinders while running on the same crank. The V series engines are available in V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 and going to a gargantuan count with variation in designs. The first V2 or V-twin engine was out in 1889 and some years later in 1903, the world had seen the first V8 engine. Boxer engine, in current times is under production with BMW Motorrad, while in cars, Subaru and Porsche are the leaders.

It is a bit striking that what made people to build another flat engine, when the V series already had one? Why this engine is named “Boxer”? As I mentioned earlier that the pistons in this engine move in contrast to each other, which also balances the whole accumulation, the prerequisite of placing a balance shaft can be omitted. The reduction in weight with the removal of this shaft reverts over the whole mechanism of the motorbike or the vehicle to raise in acceleration, performance and efficiency. As far as the name of the bike is concerned, the piston inside the engine revolves over the axis of the crank, both the transverse pistons come close to each other and act as two fighters or boxers scrambles their fist before the combat.

The BMW RnineT is the latest bike in the lineup apart from GS series motorbikes, to pump over the Boxer engine. This bike hosts an Air/oil-cooled, 4-stroke engine, two camshafts and four radially aligned valves per cylinder with a central balancer shaft. The 110hp of power gets discrete out of the 1170cc displacement engine making 119 Nm of torque at peak. The lighter crankshaft in this engine stroke 70.3mm lower than the earlier 73mm. The inlet and outlet valves have been redesigned with amended airbox, inlet and outlet channels, compressions etc. to relish out the best of BMW. The greatest positive effects of the Boxer engines can be seen in aircrafts, cars and motorbikes.